Education of the Week
By: Joshua Greentein, MD
Here is the case….
An 86-year-old male with a history of diabetes presented to the ED with left testicular pain for 2 days. Exam demonstrated left testicle enlargement, erythema, and tenderness to palpation. The patient was afebrile, with a WBC count of 9,000, and a UA with Nitrates and leukocytes. ED POCUS scrotal ultrasound was performed
What does the ultrasound show?
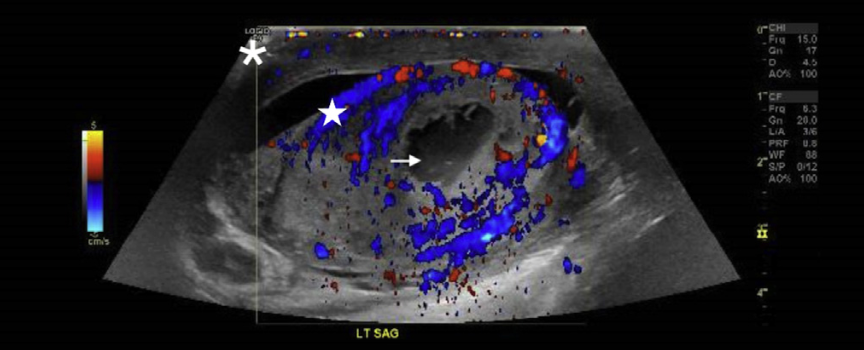
An irregular fluid collection (arrow) within the left testicle (star) as well as a reactive hydrocele (asterisk).
What does the increased vascular flow demonstrate?
Increased surrounding vascular flow demonstrates inflammatory changes (star) within the testicle. Scrotal wall thickening (asterisk), and hypoechoic structure/testicular abscess (arrow) are also seen.
What is the typical clinical presentation of an abscess?
In most cases, epididymo-orchitis has been present for some time, and thus typically patients present with testicular pain, often accompanied by fever and swelling, which has lasted a number of days. In a minority of cases, a testicular abscess can result from bacterial infection of an existing hematoma, or a region of infarction. In sexually active patients, common pathogens include Gonorrhea and Chlamydia. However, those who are not sexually active can have other gram-negative and gram-positive organisms.
What are the sonographic features of a testicular abscess?
A testicular abscess on ultrasond is typically spherical or elliptical, with a focal area of mixed echogenicity due to necrotic cellular debris. Testicular abscess may also demonstrate enlargement of the affected testicle and a reactive hydrocele. Occasionally, intrascrotal gas may be present
What is the differential diagnosis?
The differential diagnosis includes testicular torsion, epididyomo-orchitis, epididymal abscess, testicular cancer, and testicular trauma.
What is the treatment?
Treatment depends on the size of the testicular abscess and clinical parameters. Minor cases can be treated with antibiotics, while more severe cases may require surgical debridement or orchiectomy.
I love ultrasound, can you give me another resource to review this?